
2 Poop Charts
To better assist those trying to determine if their dog’s poop is something to be concerned about OR not …
… please use the following charts to help you assess your dog’s poop:

Overall, the best poo is Score #2 … however….. if you are seeing Score #3…. that is acceptable too.
If you see Score #4, 5, 6, or 7…… there is a problem and the EPI treatment protocol needs to be adjusted.
Here is another chart in PDF (please wait for the link to load) to also help you identify the poop and this chart explains what might be going on:
Dr. Becker / Mercoloa explains dog poop
https://healthypets.mercola.com/sites/healthypets/archive/2015/07/15/assessing-dog-poop.aspx
What’s ‘Normal’ Poop for Your Dog?
Generally speaking, a healthy canine stool is moist and firm, and has a mild odor.

Dogs fed processed kibble (which I don’t recommend) typically produce large quantities of voluminous poop for several reasons. First, most kibble manufacturers add unnaturally high amounts of fiber (beet pulp, soybean, and rice hulls, as well as “cellulose,” otherwise known as wood fiber, or sawdust). The normal fiber content of the ancestral diet is between 4 and 6 percent. The fiber content of many dry foods is greater than 15 percent, and most “diet” or “lite” foods contain more than 28 percent fiber.
Dogs eating kibble also produce a stinkier poop because their bodies aren’t designed to absorb certain nutrients in those diets (for example, grain and other starches, including the unnaturally high potato and pea content found in many “grain free” foods). In some instances, it can feel like your dog is passing out more volume of waste than the food volume she ate!

Raw fed dogs, on the other hand, tend to produce significantly less poop that is also smaller in size, firmer, and significantly less stinky. Dogs eating a high mineral raw food diet will produce poo that turns a much lighter color within 24 hours and disintegrates very quickly.
Dogs eating raw foods that could be too high in calcium or bone pass white, chalky feces, and may suffer from obstipation.

Regardless of your dog’s diet, it’s important to know what her poop looks and smells like normally so that you’ll be immediately aware of any changes in frequency, consistency, size, color, or smell.
One of the most obvious signs of a potential health problem in dogs is diarrhea, and diarrhea can have different characteristics depending on its cause.
Types of Dog Diarrhea
In the following situations, unless the problem clears up on its own within a day or so, I recommend making an appointment with your veterinarian.
• A soft stool with no visible blood or mucous might indicate either a dietary change or indiscriminate eating. However, it can also signal the presence of an intestinal parasite such as giardia.

• A greasy-looking gray stool can be a sign of too much fat in your dog’s diet, which can trigger pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas that can range from very mild to life threatening.

•A black, tarry stool typically indicates the presence of old blood somewhere in the dog’s digestive system. It can be a sign of injury to the GI tract from indiscriminate eating, and it can also be a sign of a very serious disease such as cancer.
•Watery diarrhea can be a sign of stress or a viral (e.g., parvovirus) or parasitic infection and can lead very quickly to dehydration, especially in puppies.

•A soft stool containing or coated with mucous may indicate the presence of parvovirus or parasites.
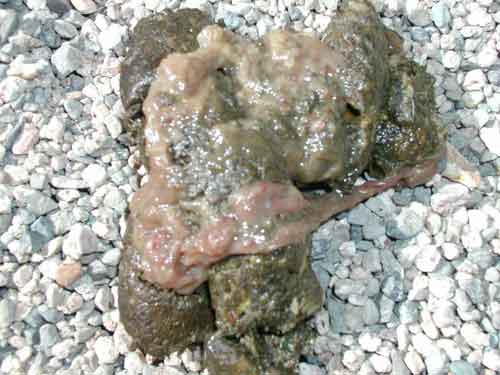
•A soft or watery stool with visible worms, eggs, or other uninvited guests is a clear indication of a parasite infestation.
•Firm, soft, or runny poop containing blood or blood clots is almost always a sign of a serious health problem requiring immediate attention. Fresh blood indicates current bleeding, typically from the large intestine or the anus or anal glands. There could be a perforation of the intestinal wall from something the dog ingested, or from the eruption of a tumor or ulcer.
Causes of Diarrhea
Since diarrhea is a symptom of multiple health problems, it also has multiple causes. These include:
| Change in diet | Toxins | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| Food intolerance, sensitivity, allergy | Idiopathic hemorrhagic gastroenteritis | Small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) |
| Intestinal parasites | Lymphangiectasia | Histoplasma enteritis or colitis |
| Indiscriminate eating | Tumors | Intestinal obstruction |
| Bacterial infection | Rectal polyps | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| Viral infection | Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency | Histiocytic ulcerative colitis |
The Not-So-Obvious Symptoms of Diarrhea
When most of us think of a dog with diarrhea, we picture the poor pup standing anxiously at the door, needing to get out quickly. Once he’s out, he dashes off to find a suitable spot and passes loose, watery stool. Alternatively, if we’re not around when the urgency hits, we come home to an accident on the floor.
But what many dog parents don’t realize is that sometimes diarrhea causes straining to go, making it look more like constipation than diarrhea. That’s because diarrhea upsets the normal rhythm of the muscle contractions in your dog’s intestinal tract, giving her the feeling that she constantly needs to poop. So even though she’s hunched over and straining, her colon might be empty after repeated bouts of loose stool.
And in cases of chronic diarrhea, many dogs don’t have accidents in the house and don’t have fecal urgency, they simply always have loose, watery stools.
Other symptoms that can go along with diarrhea include fever, lethargy, malaise, loss of appetite, and dehydration. Puppies, small dogs, and seniors are at risk of dehydration from just one round of explosive diarrhea.
Small bowel diarrhea can also be confusing to owners, as the first part of the stool is firm, followed by soft or very loose second half of the bowel movement, which can indicate a variety of issues including small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, maldigestion, malabsorption, food intolerances, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, dybiosis, or IBS.

When to Call the Vet
Most healthy dogs experience an occasional episode of loose stool or diarrhea that resolves within 12 to 24 hours. The underlying issue in most of these cases is indiscriminate eating or stress. However, any dog has the potential to become very ill from chronic bouts of diarrhea.
If your dog seems fine after a bout of diarrhea — meaning she’s acting normal, with normal energy – it’s safe to simply keep an eye on her to insure her stool returns to normal within a day or so.
But if you notice she’s also sluggish, running a fever or feels warm to the touch, or there’s a change in her behavior, you should contact your veterinarian.
If you see blood in your pet’s stool or she’s weak or shows other signs of debilitation along with the diarrhea, you should make an appointment with the vet.
If your dog seems fine but is experiencing recurrent bouts of diarrhea, it’s time for a checkup.
It’s important to bring a sample of your dog’s stool to your appointment, even if it’s watery. Use a plastic baggie and shovel a bit in there to take with you. This will help your vet identify potential underlying causes for the diarrhea.